Title
Create new category
Edit page index title
Edit category
Edit link
iOS Trust SDK Integration Guide
Introduction
This guide is aimed at developers and will provide the necessary steps for integrating with the Trust SDK. The guide offers a step by step walkthrough on how to authenticate with TrustX and start a TrustX authentication or Identity Verification process through the Trust SDK.
To complete this guide, the reader must have access to the TrustX back office application in order to create API Keys and Process definitions. If the reader does not have access to the TrustX back office application, they can request access via support@daon.com
Overview
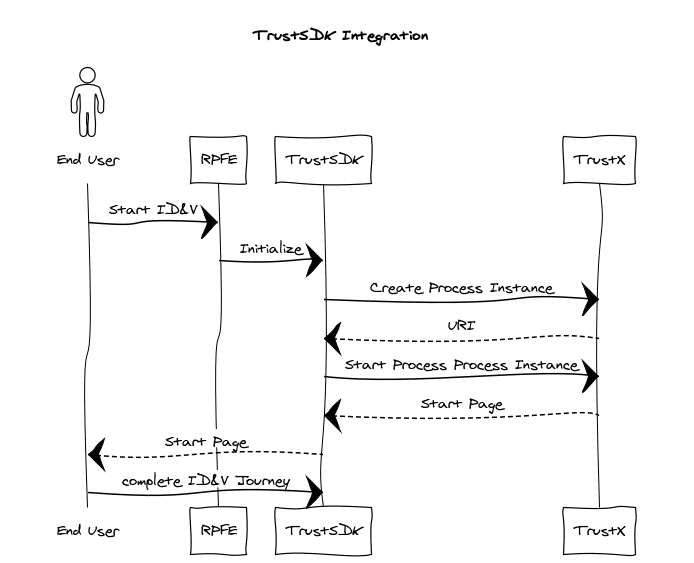
Sequence Diagram with calls for a typical integration scenario.
This guide assumes that the user is integrating from a mobile application. In summary:
The End User starts the journey on a Relying Party's application, possibly by clicking on a button or a link to start the TrustX Identity Verification and Authentication journey.
The Relying Party makes a series of calls to TrustX. These calls serve a number of purposes:
- Authenticate the relying party so that they can makes calls to TrustX.
- Create a Process Instance from a Process Definition based on a Process Token.
The mobile application has imported the Trust SDK. See iOS NFC Native Interface for more information.
Start the Process Definition and redirect the End User to TrustX so that the end user can complete the journey.
A Relying Party is a term commonly used to refer to the entity wishing to establish a claim of Identity.
Step 1. Create Token
A Token is created by invoking the API call below:
POST https://{{tenant}}.{{region}}.trustx.com/api/arthr/apiKeys/issueContent-Type: application/jsonX-API-Key: {{apiKey}}{}A token grants access to the caller to invoke API calls on TrustX. Once the token is generated it can be reused, however it must be noted that the token has a 'time to live'. Once the 'time to live' has expired a new token must be generated.
When calling the API to issue a token, you will need to provide an API Key. This API Key is obtained from an API Key's secret. See the API Key Guide for information on how to manage API keys.
When the api/arthr/apiKeys/issue API is invoked, the response to this call provides a bearer token. This bearer token is used to authenticate subsequent calls to TrustX.
The permissions required for the APIs calls within this integration guide are as follows (note: replace {tenantid} with literal value):
TNT#{tenantid}#ProcessManager:addProcessTokenTNT#{tenantid}#ProcessManager:getProcessInstanceTNT#{tenantid}#UserDataServer:getProcessInstanceUserDataTokens should be protected - they should reside only in the back end service and should not be publicly shared by embedding in web pages. If a token is compromised it can provide bad actors access to your services and data in TrustX.
Step 2. Create Process Token
A process token is used to create process instances from a Process Definition. For more information on creating a Process Definition, see the Process Definition Guide. When creating the process token the process definition name and version must be supplied.
POST https://{{tenant}}.{{region}}.trustx.com/api/process-manager/processTokensContent-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Bearer {{token}}{ "name": "My Process Token", "description": "A token that allows me to start create an instance of my process definition", "status": "ACTIVE", "type": "MULTI_USE_COUNT_LIMITED", "maxCount": 1, "processDefnName": "{{processDefnName}}", "processDefnVersion": "{{processDefnVersion}}", "uiUrl": "https://{{tenant}}.{{region}}.trustx.com/web/trustweb", "parameters": { "email": "myemail@daon.com", "_redirectUrl": "https://www.daon.com" }}When creating a process instance, extra parameters can be passed to provide additional information about the process. For example, the End User's details such as email, phone, first-name, surname, etc. can be passed as parameters. See the API Guide for more information.
Process Token Resource
The process token resource above contains the following attributes. See the API Guide for more information.
| Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | A unique name to describe the process token. |
| description | string | A short description of the token |
| status | string | The process token status. In the example above we create the token to be active. Valid values: ACTIVE,INACTIVE |
| type | string | The process token status. In the example above we create the token to be active. Valid values: UNLIMITED, MULTI_USE COUNT_LIMITED,_ MULTI_USE_TIME_LIMITED |
| maxCount | number | The number of times the token can be used. In the example above the token can be used once only. |
| processDefnName | string | The process definition name. Using the combination of process definition name and process definition version a specific process definition is bound to the process token to be used when a process instance created with a token (See Step 3.) |
| processDefnVersion | string | The process definition version. Using the combination of process definition name and process definition version a specific process definition is bound to the process token to be used when a process instance created with a token (See Step 3.) |
| uiUrl | string | The URI of the application to execute the process definition when the process instance is started. Currently on TruxtX user interfaces are supported. |
| parameters | Map<String,String> | A map of additional parameters can be supplied to provide extra information when the process instance is started. This additional parameter map could typically contain information such as:
These are typically attributes that are useful for searching for an ID&V applicant. Any set of additional parameters may be passed in. |
Step 3. Create Process Instance
Once a Process Token is created, it can be used to create the Process Instance.
POST https://{{tenant}}.{{region}}.trustx.com/api/process-manager/processInstances/create?pt={{ptoken}}Content-Type: application/jsonAuthorization: Bearer {{token}}The response provides the redirect URL that is then used to start the process definition.
Optional - Set Default Language
It is possible to set the default language by appending the redirect URL with the lang query parameter. This query parameter accepts an ISO language code as input in the format: redirectUrl + "&lang=<ISO language code>"
Example:
https://skyprod.oak.trustx-dev.com/web/trustweb/?pt=7BU2B6IHVVCZWE2PM5JMZW7GUE&lang=it
Step 5. Initializing the Trust SDK
With the URL generated, the Trust SDK can be initialized.
- Initialize the DaonTrustSDK:
let sdk = TrustSDK(withViewController: self, delegate: self)- Daon Trust SDK offers setting a DaonOptions object for customization purposes. You can set your own initialization timeout as well as the URL of the environment that you want to use:
let options = DaonOptions()options.serverUrl = "https://www.example.com"options.initializationTimeout = 15If you do not set the DaonOptions object, default values will be used. Initialization timeout default value is '10'. By not setting the custom environment URL, you are requesting of the Daon Trust SDK to launch a QR code scanning feature which expects the QR code that carries the URL of your environment as a value.
- Finally, you can start the Onboarding process by calling 'start()' function of the TrustSDK:
sdk.start(withDaonOptions: options)Step 6. End User completes Journey
The end user will be redirected to TrustX where they can complete the Identity Verification and Authentication journey as defined in the Process Definition.
Step 7. Getting Process Instance Status
Once the user has completed the journey the status of the process instance can be checked.
GET https://{{tenant}}.{{region}}.trustx.com/api/process-manager/processInstances/{{processInstanceId}}Authorization: Bearer {{token}}Alternatively webhooks can be used to get notification about the process instance at any stage in the process definition. For information on webhooks see the Webhooks Guide.
Step 8. Getting End User's provided Data
GET https://{{tenant}}.{{region}}.trustx.com//api/userdata-server/processDefinitions/{processDefnId}/processInstances/{processInstanceId}/userdataAuthorization: Bearer {{token}}| Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|
| processDefnId | String | The id of the process definition. This is generated when creating the process definition |
| processInstanceId | String | The id of the process instance. This is generated when creating the process instance. |
Optional: Appkeys Integration
Appkeys utilize the FIDO Universal Authentication Framework (UAF) specification to provide a passwordless solution to registration and authentication where an identity is bound to only one device or biometric profile without the need for passwords or QR codes.
To take full advantage of Appkeys in TrustX, it is necessary to integrate the FIDO SDK with the Trust SDK to
- Store Appkeys on a device for stronger security than the web-based alternative.
- Capture biometrics (face, fingerprint) to complete biometric-bound registration and authentication flows with Appkeys.
This document will describe the configuration steps to include the FIDO SDK with your iOS application.
Dependencies
Add your GitHub account to Xcode and add the xAuth FIDO SDK as a Swift Package.
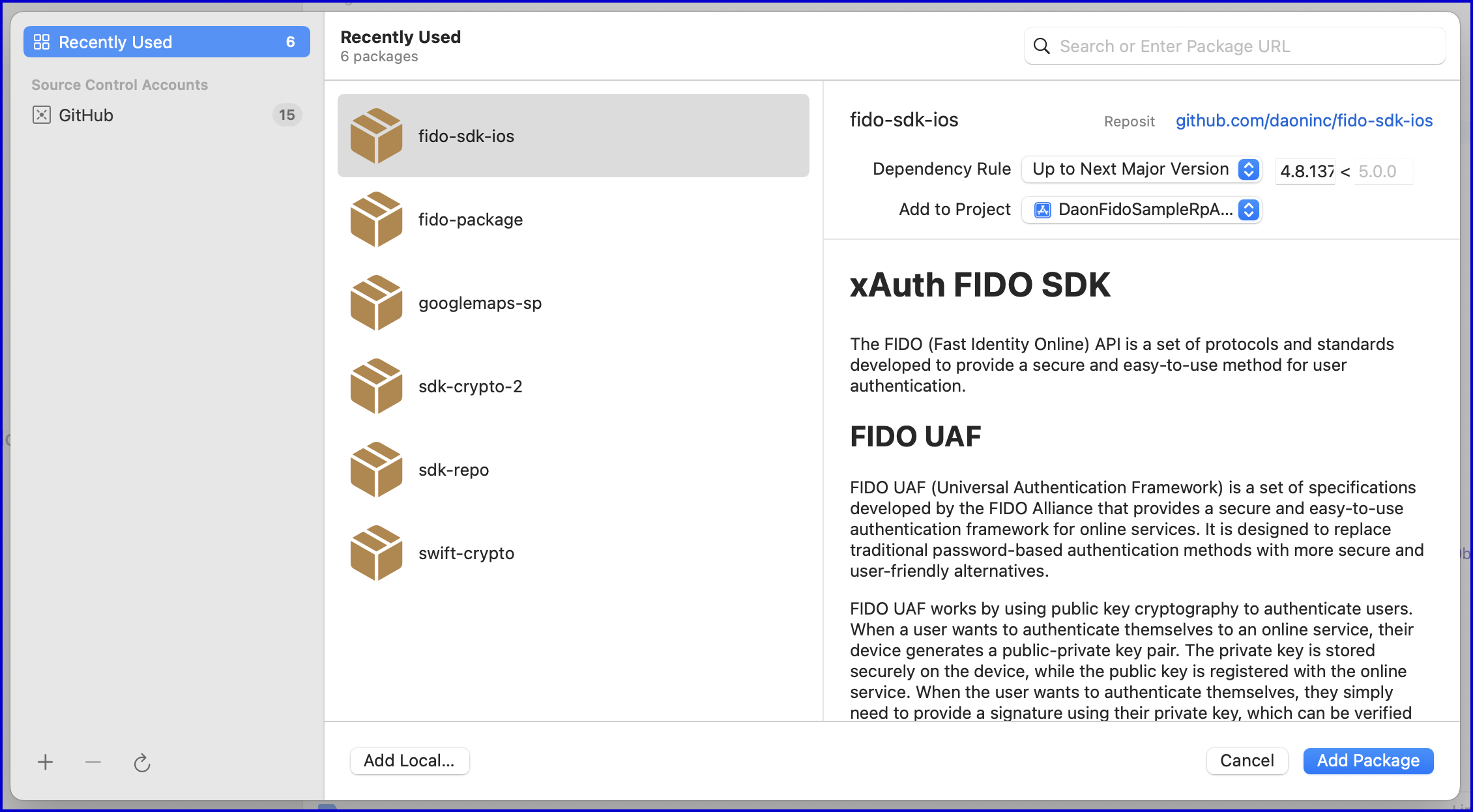
It is not required to include every FIDO package as currently only the DaonFIDOSDK library is required.
Example:
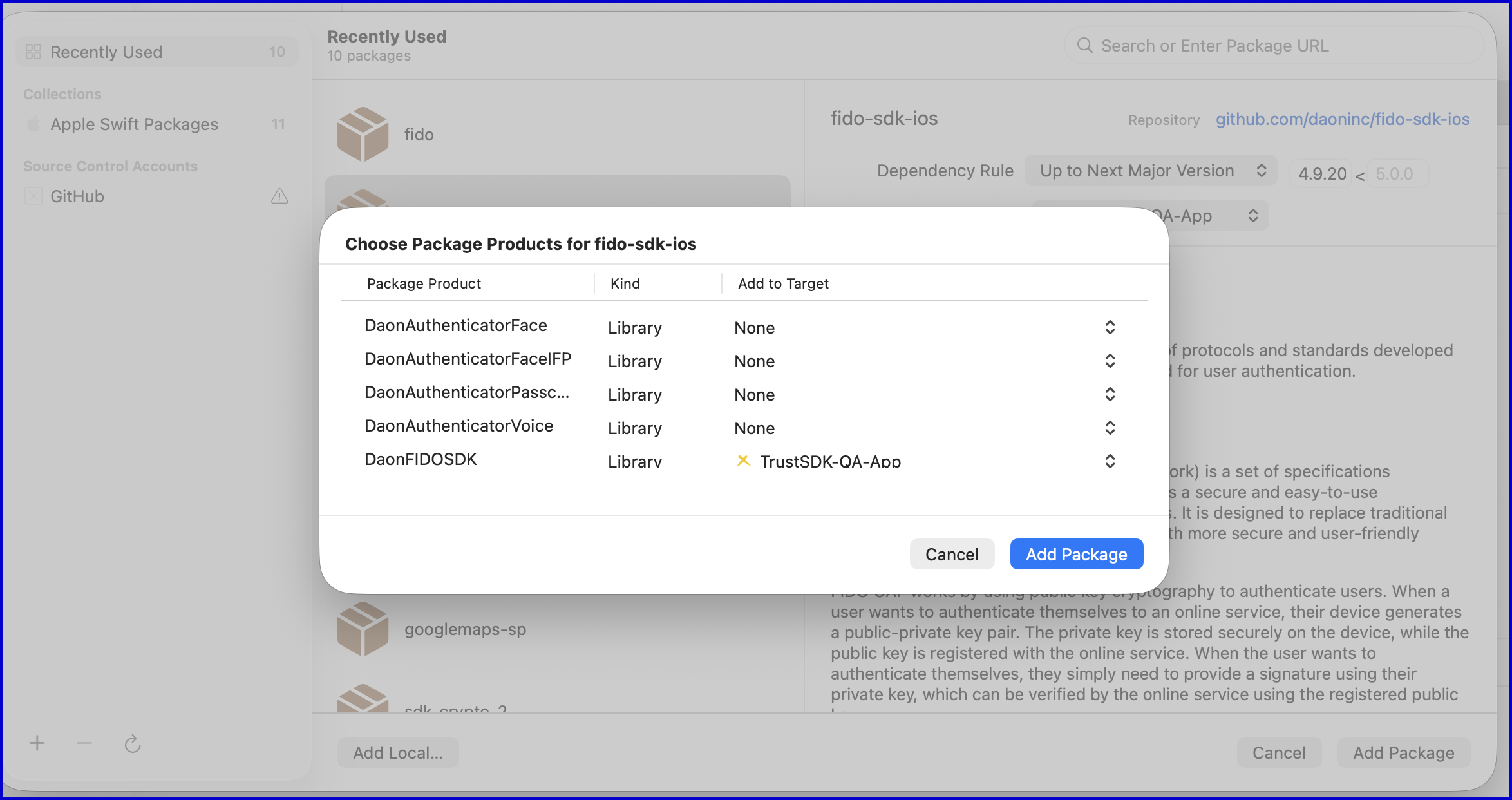
It is then possible to add the FIDO SDK dependencies to the Trust SDK.
Example:
import DaonTrustAppkeysProcessordo { let appkeysProcessor = try AppkeysProcessor.Builder() .enableDebugLogs(false) .enableLocationUsage(false) .enableSilentBiometricRegistration(false) .setBiometricRegistrationReason(“Registration Reason”) .setBiometricAuthenticationReason(“Authentication Reason”) .build() sdk.addAppkeysProcessor(appkeysProcessor)} catch { // Handle builder error}Optional: NFC Integration
The Daon Trust SDK Document Processor provides features to perform OCR of MRZ from document images and NFC scanning of passports and other documents.
This section will describe how to add the Document Processor and add the processor to your project.
Step 1. Add the Processor
To add the Document Processor to your project, perform the steps outlined below.
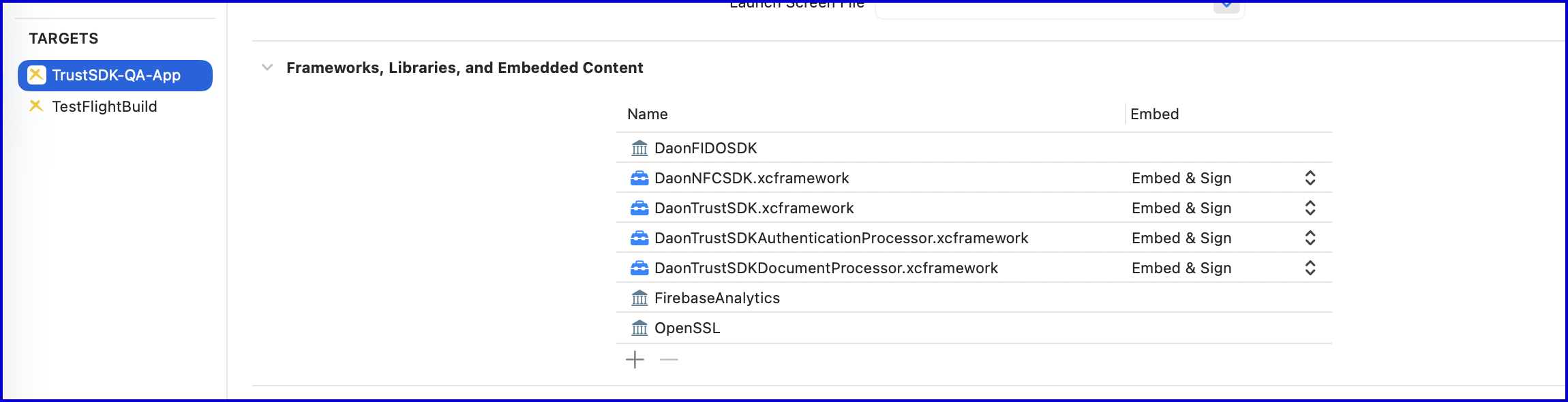
- Add the following frameworks to your application target under
_Frameworks > Libraries > Embedded Content_:
- DaonTrustSDKDocumentProcessor.xcframework`
- DaonNFCSDK.xcframework`
- Ensure that once added, the frameworks are marked as 'Embed & Sign'
Additionally, the OpenSSL library should be added via Swift Package Manager.
To install OpenSSL using Swift Package Manager, follow the steps outlined in Apple's Official Documentation using the URL for the OpenSSL repo with the version: 1.1.2300
- In Xcode, select 'File > Add Packages...'
- Enter: https://github.com/krzyzanowskim/OpenSSL.git
Alternatively, this can be added in the dependencies of the Package.swift file_:_
dependencies: [ .package(url: "https://github.com/krzyzanowskim/OpenSSL.git", from: "1.1.2300")]Step 2. Configure the Processor
To create a new instance of the Document Processor you must use the ``DocumentProcessor/Builder class which allows you to configure and then build the processor using method chaining. The document processor can then be added to the Trust SDK instance.
import DaonTrustSDKDocumentProcessor...do { // OPTIONAL: Add Document Processor to SDK for MRZ OCR and NFC Passport scanning. let documentProcessor = try DocumentProcessor.Builder() // Call configuration methods, e.g. .setLicense() .build() // Add the Document Processor to the Trust SDK instance sdk.addDocumentProcessor(documentProcessor)} catch { // Handle builder error}Once configured, the process can be started by performing the following:
sdk.start(withDaonOptions: options)